Graphs
A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview
Implementation of Graph in JavaScript
ExcerptA Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
In this article we would be implementing the Graph data structure in JavaScript. Graph is a non-linear data structure. A graph G contains a set of vertices V and set of Edges E. Graph has lots of application in computer science. Graph is basically divided into two broad categories : \
Directed Graph (Di- graph) – Where edges have direction.
Undirected Graph – Where edges do not represent any directed
There are various ways to represent a Graph :- \
Hey geek! The constant emerging technologies in the world of web development always keeps the excitement for this subject through the roof. But before you tackle the big projects, we suggest you start by learning the basics. Kickstart your web development journey by learning JS concepts with our JavaScript Course. Now at it's lowest price ever!
Adjacency Matrix
Adjacency List
There are several other ways like incidence matrix, etc. but these two are most commonly used. Refer to Graph and its representations for the explanation of Adjacency matrix and list. In this article, we would be using Adjacency List to represent a graph because in most cases it has a certain advantage over the other representation. Now Lets see an example of Graph class- \
JavaScript
JavaScript
class Graph {
constructor(noOfVertices)
{
this``.noOfVertices = noOfVertices;
this``.AdjList = new Map();
}
}
The above example shows a framework of Graph class. We define two private variable i.e noOfVertices to store the number of vertices in the graph and AdjList, which stores a adjacency list of a particular vertex. We used a Map Object provided by ES6 in order to implement Adjacency list. Where key of a map holds a vertex and values holds an array of an adjacent node. Now let’s implement functions to perform basic operations on the graph: \
addVertex(v) – It adds the vertex v as key to adjList and initialize its values with an array. \
JavaScript
JavaScript
addVertex(v)
{
this``.AdjList.set(v, []);
}
addEdge(src, dest) – It adds an edge between the src and dest. \
JavaScript
JavaScript
addEdge(v, w)
{
this``.AdjList.get(v).push(w);
this``.AdjList.get(w).push(v);
}
In order to add edge we get the adjacency list of the corresponding src vertex and add the dest to the adjacency list.
printGraph() – It prints vertices and its adjacency list. \
JavaScript
JavaScript
printGraph()
{
var get_keys = this``.AdjList.keys();
for (``var i of get_keys)
{
var get_values = this``.AdjList.get(i);
var conc = ""``;
for (``var j of get_values)
conc += j + " "``;
console.log(i + " -> " + conc);
}
}
Lets see an example of a graph\
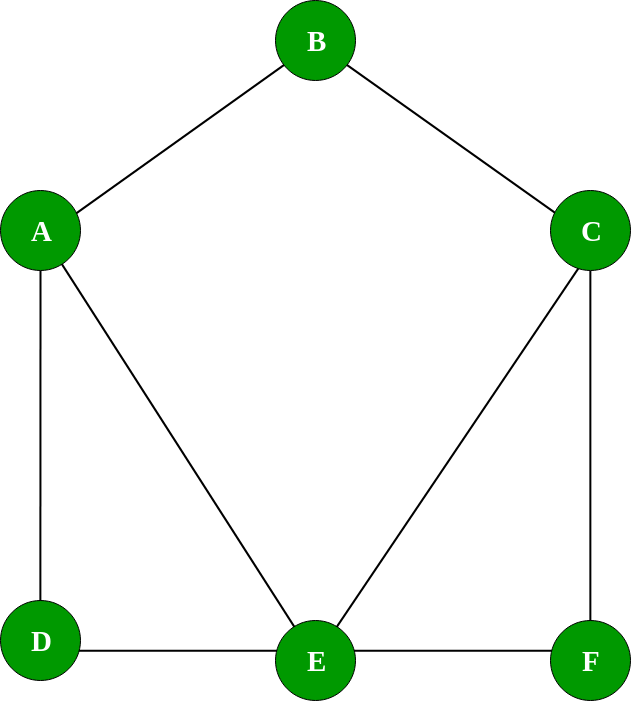
Now we will use the graph class to implement the graph shown above: \
JavaScript
JavaScript
var g = new Graph(6);
var vertices = [ 'A'``, 'B'``, 'C'``, 'D'``, 'E'``, 'F' ];
for (``var i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
g.addVertex(vertices[i]);
}
g.addEdge(``'A'``, 'B'``);
g.addEdge(``'A'``, 'D'``);
g.addEdge(``'A'``, 'E'``);
g.addEdge(``'B'``, 'C'``);
g.addEdge(``'D'``, 'E'``);
g.addEdge(``'E'``, 'F'``);
g.addEdge(``'E'``, 'C'``);
g.addEdge(``'C'``, 'F'``);
g.printGraph();
Graph Traversal
We will implement the most common graph traversal algorithm: \
Implementation of BFS and DFS: \
bfs(startingNode) – It performs Breadth First Search from the given startingNode \
JavaScript
JavaScript
bfs(startingNode)
{
var visited = {};
var q = new Queue();
visited[startingNode] = true``;
q.enqueue(startingNode);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
var getQueueElement = q.dequeue();
console.log(getQueueElement);
var get_List = this``.AdjList.get(getQueueElement);
for (``var i in get_List) {
var neigh = get_List[i];
if (!visited[neigh]) {
visited[neigh] = true``;
q.enqueue(neigh);
}
}
}
}
In the above method we have implemented the BFS algorithm. A Queue is used to keep the unvisited nodes Lets use the above method and traverse along the graph \
JavaScript
JavaScript
console.log(``"BFS"``);
g.bfs(``'A'``);
The Diagram below shows the BFS on the example graph:\
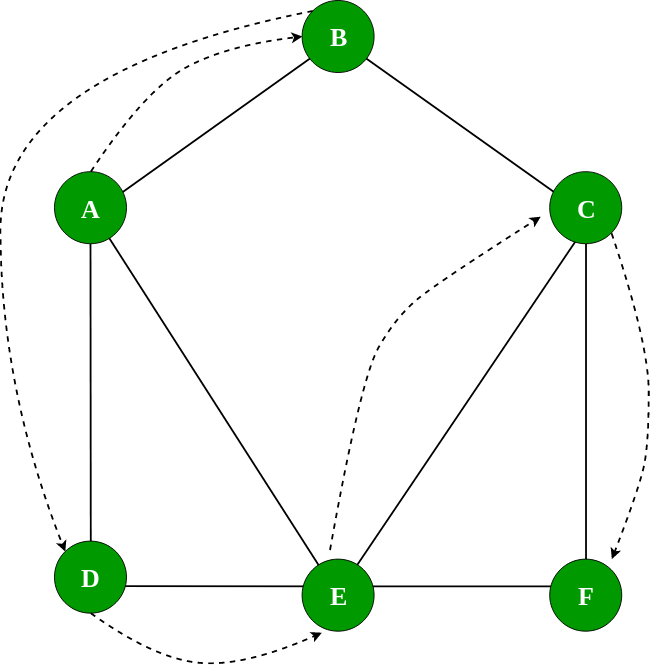
dfs(startingNode) – It performs the Depth first traversal on a graph \
JavaScript
JavaScript
dfs(startingNode)
{
var visited = {};
this``.DFSUtil(startingNode, visited);
}
DFSUtil(vert, visited)
{
visited[vert] = true``;
console.log(vert);
var get_neighbours = this``.AdjList.get(vert);
for (``var i in get_neighbours) {
var get_elem = get_neighbours[i];
if (!visited[get_elem])
this``.DFSUtil(get_elem, visited);
}
}
In the above example dfs(startingNode) is used to initialize a visited array and DFSutil(vert, visited) contains the implementation of DFS algorithm Lets use the above method to traverse along the graph \
JavaScript
JavaScript
console.log(``"DFS"``);
g.dfs(``'A'``);
The Diagram below shows the DFS on the example graph \
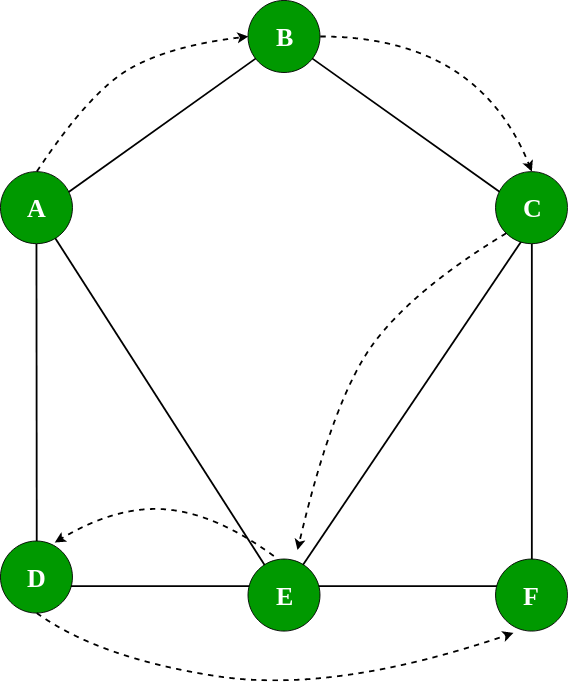
Last updated