Plugins, Themes, & Starters
TABLE OF CONTENTS
In the Gatsby ecosystem, there’s more than one way to build a site. To help you understand the differences between plugins, themes, and starters, this guide will talk through some of the details.
What is a plugin?
Gatsby plugins are Node.js packages that implement Gatsby APIs and are commonly installed through a registry like npm. There are many types of plugins, including data sourcing, SEO, responsive images, offline support, support for Sass, TypeScript, sitemaps and RSS, Google Analytics, and more. You can also make your own plugins and either distribute them for fellow Gatsby developers to use or install them locally.
What is a theme?
A Gatsby theme is a type of plugin that includes a gatsby-config.js file and adds pre-configured functionality, data sourcing, and/or UI code to Gatsby sites. Since they are plugins, themes can be packaged and distributed through a registry like npm or yarn, and versions can be updated through a site’s package.json file.
With a Gatsby theme, all of your default configuration (shared functionality, data sourcing, design) is abstracted out of your site and into an installable package. A theme might differ from a typical plugin in that it packages up usage of a plugin into a consumable API, making it possible to include functionality without having to type out all of the code by hand (such as GraphQL queries). To understand more of the motivation for Gatsby themes, check out the docs on What are Gatsby Themes?
What is a starter?
A starter is a boilerplate Gatsby site that users can copy and customize. Once modified, a starter maintains no connection to its source.
Gatsby offers official starters for a default site, blog site, bare-bones hello world site, and both using and creating themes. There are also many starters from members of the community that can provide a good starting point for your Gatsby site.
Conventions for usage
Themes are a type of plugin, making both themes and plugins capable of the same functionality. The difference between them is intended usage. Themes are intended to own a piece of the site (like an about us page), whereas a plugin is intended to modularize Gatsby APIs into smaller pieces. Themes tend to cover a broader scope of responsibility, packaging up multiple behaviors, where plugins are meant for more specific functionality.
Starters are generally used as the starting point that plugins and themes are then installed into. However, they’re based on one-time use and do not get updated over time as plugins and themes do.
Comparing differences
Once you have a conceptual understanding of what a plugin, theme, and starter is, you may ask yourself what each is suited for in relation to each other.
The following tables put plugins, themes, and starters side-by-side, showing what each is more appropriate for.
Legend
●
Fully capable (possible and supported)
◐
Somewhat capable (support is minimal or it is not best practice)
○
Not capable
Differences and considerations in maintenance
When it comes to maintaining a Gatsby site, plugins and themes offer a distinct advantage to starters by being distributed as packages. This means making changes in multiple Gatsby sites is done by a new install of an updated package upstream. It’s difficult to sync changes across multiple sites derived from the same starter.
Versioning
●
●
◐
Install as Package
●
●
○
Versioning
Starters can still be versioned inside of a repository so that you can track issues or bugs associated with specific updates, but they aren’t formally released and published, so they aren’t versioned like a plugin or theme is.
Installing as a package
Starters can’t be installed into existing sites, this limitation was one of the motivating factors in developing the newer concept of themes. You can read more about the rationale for themes in the What are Gatsby Themes guide.
Differences and considerations in configuration
Plugins and themes can expose options to make them configurable for users. There are different possibilities for configuration like passing in options and shadowing files that make plugins and themes more powerful—but also more complicated—than starters. Because themes are also plugins, shadowing is possible in plugins as well. It may make sense for a plugin to take advantage of the shadowing API, but it is less common.
Pass in Options
●
●
◐
Shadowing
◐
●
○
Uses Multiple Plugins
◐
●
●
Custom components
◐
●
●
Pass in Options
Plugins and themes both allow options to be passed in when installed in the plugins array of a gatsby-config. Starters can be set up with documented options for customization, but there are no officially supported options for starters apart from what the author of the starter decides to write.
Shadowing
Theme shadowing exists to allow users to override or otherwise extend individual components provided by a theme. For example, a plugin or theme can provide a specific path to gatsby-config so the plugin knows where to build pages from, but the user wouldn’t be able adjust how those pages are built, only from what path. Theme shadowing allows users to replace a file with their own version of it, allowing them to rewrite that logic to use the path in a different way.
An example of a plugin that uses shadowing is gatsby-plugin-theme-ui which allows you to shadow a theme file to use in your own theme.
Starters aren’t capable of shadowing (and they don’t need to be), because a user of a starter can adjust any file by editing it directly.
Uses multiple plugins
Themes are intended to abstract several plugins into one, by making a gatsby-config that a Gatsby site will run along with its own config. Starters can also be configured with multiple plugins so someone can get up and running without worrying about configuring too many loose ends.
Custom components
Custom components are most traditionally distributed as packages in the React ecosystem. Components don’t need to hook into the Gatsby build system, so if shipped with a plugin they don’t need to be included in a gatsby-config’s plugin array. This is the case with gatsby-image which is a React component. It doesn’t need to be included in the plugins array because it is merely a component.
Some plugins ship with components you can use in a Gatsby site. An example is the <OutboundLink />component fromgatsby-plugin-google-analytics. Other plugins, like gatsby-plugin-react-helmet, require you to install components from other libraries.
Themes by convention are more suited to ship with components that could then be shadowed for customization.
Starters will include components to render data, but they are tied to the starter.
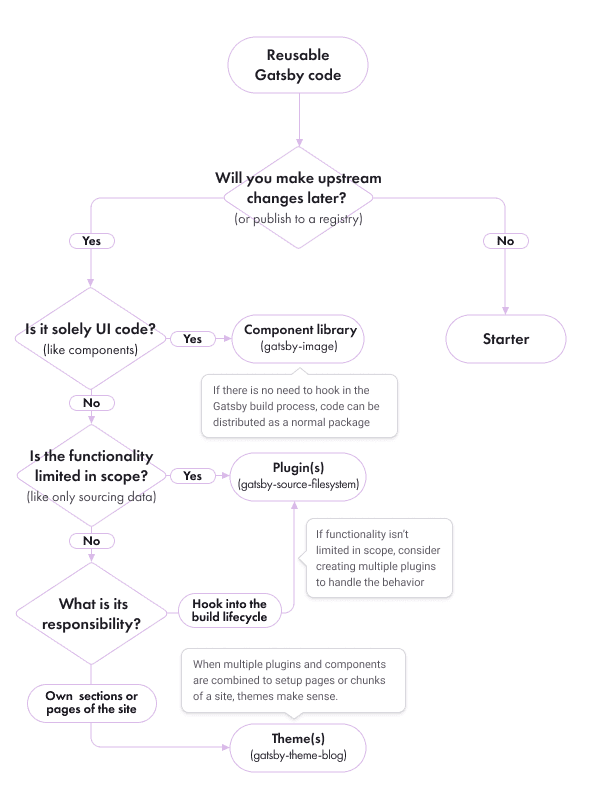
Deciding which to use
As an aid to help try and guide you to which of the 3 options is right for your use case, consider this flowchart:
Last updated